A green roof or rooftop solar? You can combine them in a biosolar roof, boosting both biodiversity and power output.

Image: Adobe Stock
Growing city populations and limited space are driving the adoption of green roofs and green walls covered with living plants. As well as boosting biodiversity, green roofs could play another unexpectedly valuable role by increasing the electricity output of solar panels.
As solar panels heat up beyond 25℃, their efficiency decreases markedly. Green roofs moderate rooftop temperatures. So we wanted to find out: could green roofs help with the problem of heat reducing the output of solar panels?
Our research compared a “biosolar” green roof – one that combines a solar system with a green roof – and a comparable conventional roof with an equivalent solar system. We measured the impacts on biodiversity and solar output, as well as how the plants coped with having panels installed above them.
The green roof supported much more biodiversity, as one might expect. By reducing average maximum temperatures by about 8℃, it increased solar generation by as much as 107% during peak periods. And while some plant species outperformed others, the vegetation flourished.
These results show we don’t have to choose between a green roof or a solar roof: we can combine the two and reap double the rewards.
Daramu House in the Sydney CBD has a large array of solar panels installed over a green roof.
How was the study done?
Many studies have tested a single rooftop divided into “green roof” and “non-green roof” sections to measure the differences caused by vegetation. A problem with such studies is “spatial confounding” – the effects of two nearby spaces influencing one another. So, for example, the cooler green roof section could moderate the temperature of the non-green section next to it.
In studies that use distinct buildings, the buildings might be too far apart or too different in construction to be comparable.
The two buildings in our study were the same height, size and shape and located next to each other in Sydney’s central business district. The only difference was Daramu House had a green roof and International House did not.
We selected a mix of native and non-native grasses and non-woody plants, which would flower across all seasons, to attract diverse animal species.
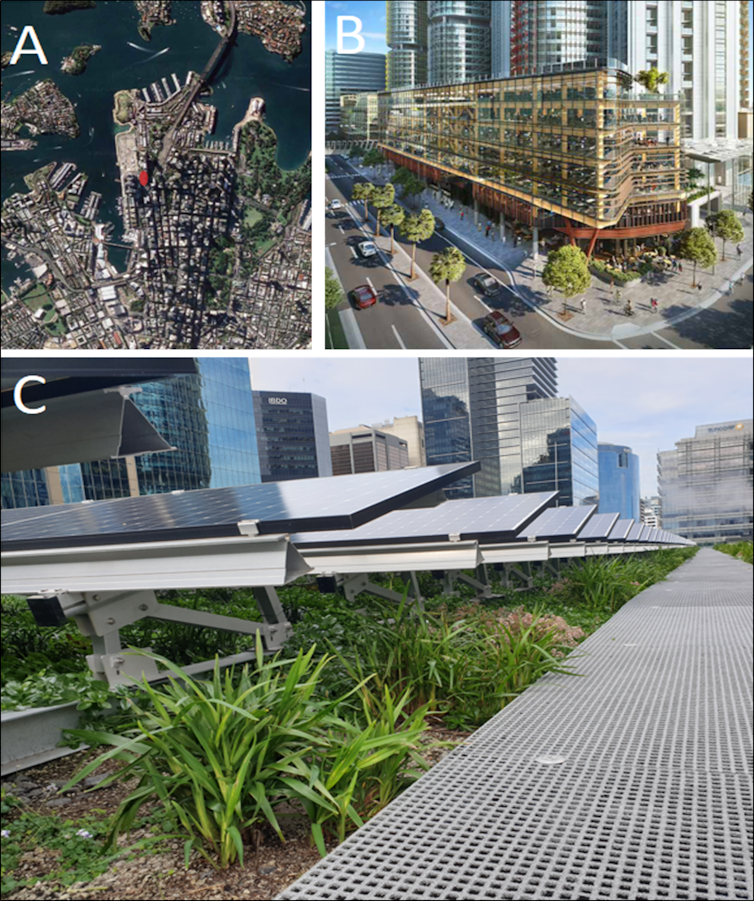 (A) The study site location (red dot) in the Sydney central business district. (B) Architectural design of Daramu House. (C) Rooftop view looking south, showing plantings around and underneath solar panels. Green Roof & Solar Array – Comparative Research Project
(A) The study site location (red dot) in the Sydney central business district. (B) Architectural design of Daramu House. (C) Rooftop view looking south, showing plantings around and underneath solar panels. Green Roof & Solar Array – Comparative Research Project
The biosolar green roof and conventional roof had the same area, about 1860 square metres, with roughly a third covered by solar panels. Vegetation covered about 78% of the green roof and the solar panels covered 40% of this planted area.
To identify which species were present on the roofs we used motion-sensing cameras and sampled for DNA traces. We documented changes in the green roof vegetation to record how shading by the solar panels affected the plants.
How did the panels affect the plants?
In the open areas, we observed minimal changes in the vegetation cover over the study period compared to the initial planted community.
Plant growth was fastest and healthiest in the areas immediately around the solar panels. Several species doubled in coverage. We selected fast-growing vegetation for this section to achieve full coverage of the green roof beds as soon as possible.
The vegetation changed the most in the areas directly below and surrounding the solar panels. The Baby Sun Rose, Aptenia cordifolia, emerged as the dominant plant. It occupied most of the space beneath and surrounding the solar panels, despite having been planted in relatively low densities.
This was surprising: it was not expected the plants would prefer the shaded areas under the panels to the open areas. This shows that shading by solar panels will not prevent the growth of full and healthy roof gardens.
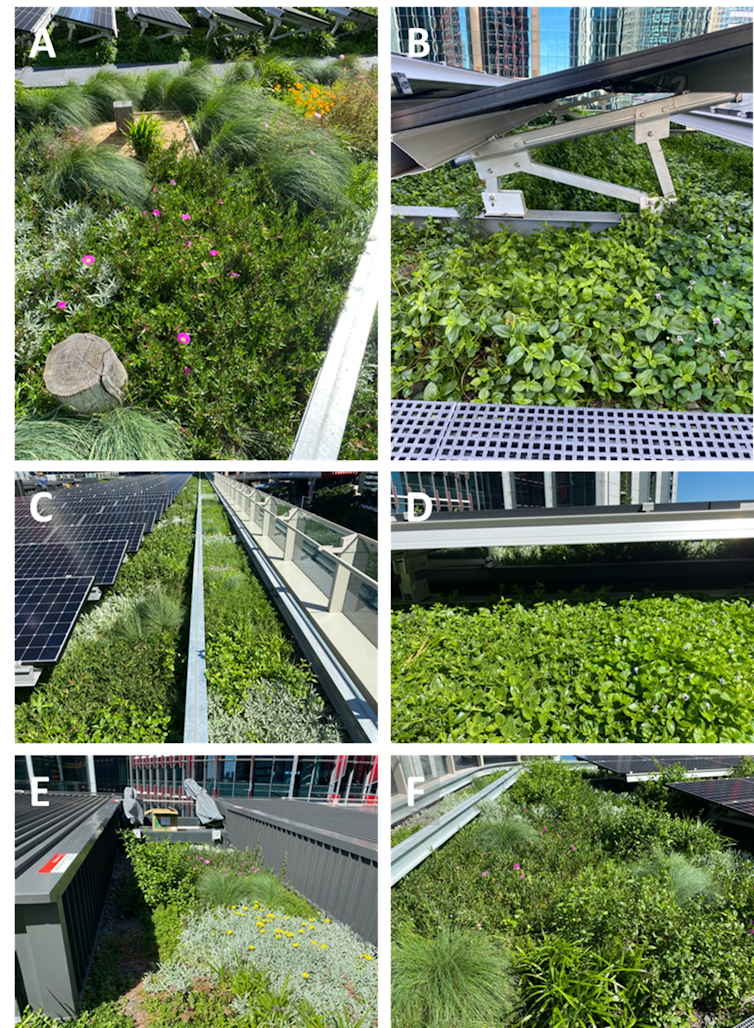 (A) An example of evenly distributed plant cover around solar panels. (B) Aptenia cordifolia (Baby Sun Rose) came to dominate the area beneath solar panels. Minor cover of Viola hederacea can also be seen. (C) Vegetation around solar panels along the outside of east section of the roof. (D) Additional evidence of the dominance of A. cordifolia beneath the panels and dieback directly under them. (E) Relatively even cover of a range of species and marked increase in height in Goodenia ovata (Hop Goodenia). (F) Substantial height increases for the entire vegetation community. Green Roof & Solar Array – Comparative Research Project
(A) An example of evenly distributed plant cover around solar panels. (B) Aptenia cordifolia (Baby Sun Rose) came to dominate the area beneath solar panels. Minor cover of Viola hederacea can also be seen. (C) Vegetation around solar panels along the outside of east section of the roof. (D) Additional evidence of the dominance of A. cordifolia beneath the panels and dieback directly under them. (E) Relatively even cover of a range of species and marked increase in height in Goodenia ovata (Hop Goodenia). (F) Substantial height increases for the entire vegetation community. Green Roof & Solar Array – Comparative Research Project
What were the biodiversity impacts?
We used environmental DNA (eDNA) surveys to compare biodiversity on the green roof and conventional roof. Water run-off samples were collected from both roofs and processed on site using portable citizen scientist eDNA sampling equipment to detect traces of DNA shed by the species on the roof.
The eDNA surveys detected a diverse range of species. These included some species (such as algae and fungi) that are not easily detected using other survey methods. The results confirmed the presence of bird species recorded by the cameras but also showed other visiting bird species went undetected by the cameras.
Overall, the green roof supported four times as many species of birds, over seven times as many arthropods such as insects, spiders and millipedes, and twice as many snail and slug species as the conventional roof. There was many times the diversity of microorganisms such as algae and fungi.
Encouragingly, the green roof attracted species unexpected in the city. They included blue-banded bees (Amegilla cingulata) and metallic shield bugs (Scutiphora pedicellata).
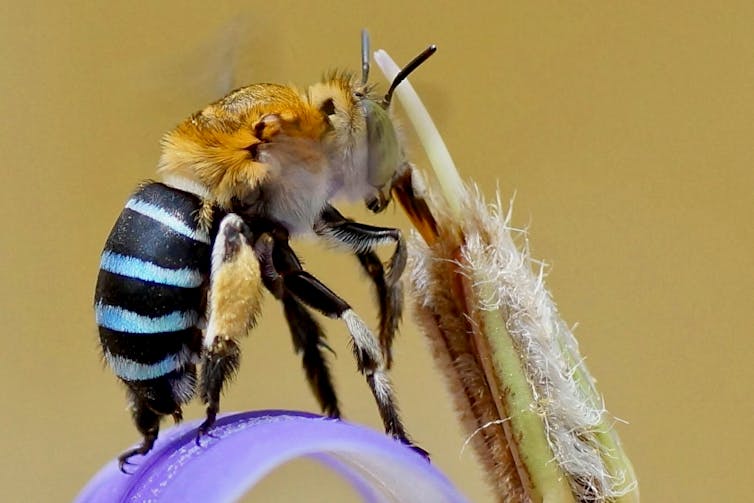 Blue-banded bees were among the unexpected visitors to the green roof. Chiswick Chap/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
Blue-banded bees were among the unexpected visitors to the green roof. Chiswick Chap/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
How did the green roof alter temperatures?
The green roof reduced surface temperatures by up to 9.63℃ for the solar panels and 6.93℃ for the roof surfaces. An 8℃ reduction in average peak temperature on the green roof would result in substantial heating and cooling energy savings inside the building.
This lowering of temperatures increased the maximum output of the solar panels by 21-107%, depending on the month. Performance modelling indicates an extensive green roof in central Sydney can, on average, produce 4.5% more electricity at any given light level.
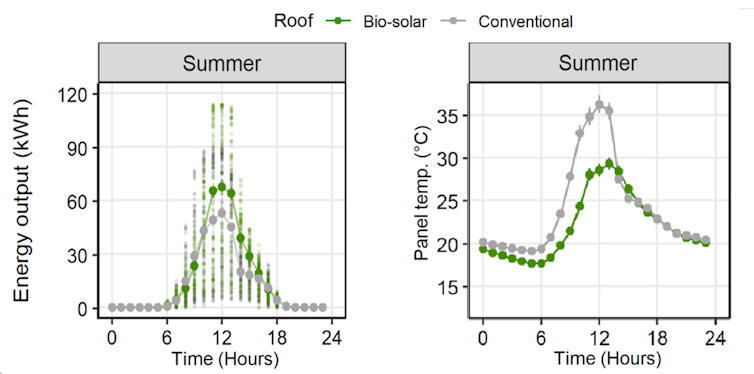 Energy output (left) and surface temperatures (right) of solar panels on a biosolar green roof and on a conventional roof. Data: Green Roof & Solar Array – Comparative Research Project
Energy output (left) and surface temperatures (right) of solar panels on a biosolar green roof and on a conventional roof. Data: Green Roof & Solar Array – Comparative Research Project
These results show we don’t have to choose between a green roof or a solar roof. We can combine them to take advantage of the many benefits of biosolar green roofs.
Biosolar roofs can help get cities to net zero
The next step is to design green roofs and their plantings specifically to enhance biodiversity. Green roofs and other green infrastructure may alter urban wildlife’s activities and could eventually attract non-urban species.
Our green roof also decreased stormwater runoff, removed a range of run-off pollutants and insulated the building from extremes of temperature. A relatively inexpensive system provides all of these services with moderate maintenance and, best of all, zero energy inputs.
Clearly, biosolar green roofs could make major contributions to net-zero cities. And all that’s needed is space that currently has no other use.![]()
Peter Irga, ARC DECRA Fellow and Lecturer in Air and Noise Pollution, School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Technology Sydney; Eamonn Wooster, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Gulbali Institute, Charles Sturt University; Fraser R Torpy, Director, Plants and Environmental Quality Research Group, University of Technology Sydney; Jack Rojahn, PhD Candidate, Institute for Applied Ecology, University of Canberra, and Robert Fleck, Research Scientist, School of Life Sciences, University of Technology Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.


