Project results
Virtual trials
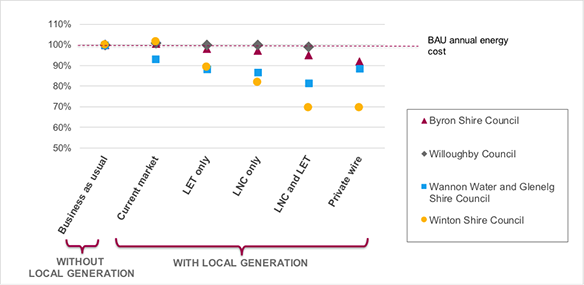
Results of five virtual trials of Local Network Charges and Local Electricity Trading indicate there is potential for distributed generation to meet local consumption, which is unlikely to be realised under current market conditions. Cogeneration in particular is likely to be undersized without incentives to export, even when such exports would be most beneficial to the grid. The Willoughby trial results demonstrate that even a relatively low Local Network Charge can send a meaningful signal to operate dispatchable generation when the network is most likely to need support.
Proponent total energy costs under each scenario.
Offering a Local Network Charge for the cases investigated would keep kWh on the grid in an era of increasingly locally derived supply. A Local Network Charge would maintain the network charges paid by the proponent, relative to a significant increase in behind the meter consumption using a private wire approach, even taking into account payment of the Local Network Charge itself. The proponent and other customers are better off, as money is not wasted on infrastructure duplication.
Download comprehensive virtual trials results:
- Virtual Trials of Local Network Charges and Local Electricity Trading - Summary Report
- Local Network Charges and Local Electricity Trading: Byron Shire Council trial fact sheet
- Byron trial case study report
- Download the business case spreadsheet for the Byron virtual trial (large file 36MB) The business case spreadsheets from other trials are available on request.
- Local Network Charges and Local Electricity Trading: Wannon trial fact sheet
- Wannon trial case study report
- Local Network Charges and Local Electricity Trading: Willoughby trial fact sheet
- Willoughby trial case study report
- Local Network Charges and Local Electricity Trading: Winton trial fact sheet
- Winton trial case study report
- Virtual trial of local electricity trading and local network credits: a community solar farm
- Download the business case spreadsheet for the Moira and Swan Hill virtual trial. The business case spreadsheets from other trials are available on request.
Economic modelling
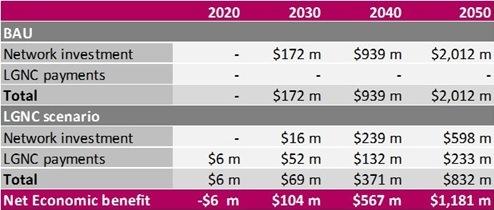
The results of the economic modelling show that over the long term a Local Network Charge (modelled as a Local Generation Network Credit – LGNC) has an overall positive economic benefit of approximately $1.2 billion, approximately 59% lower than the cost of network expansion under Business as Usual. The table below shows the net present value (NPV) of the cumulative network investment under each scenario, and the NPV of cumulative LGNC payments in the LGNC scenario.
The research found that benefits were maximised by restricting the LGNC payments to systems between 10kW and 30 MW, and this range was used in the modelling. The inclusion of smaller generators had a large cost attached, and is unlikely to be a significant incentive for these systems as the annual payments would be small compared to minor variations in the cost of PV systems.
Cumulative economic cost or benefit of an LGNC payment.
Impact on customer bills
Over the short term (2020) there is no impact on the residential sector, a modest increase of $2 per annum on average in the small commercial sector, and an increase of $25 on average in the large commercial sector in the LGNC scenario relative to BAU. By 2030 all consumers realise modest savings. The LGNC scenario as modelled represents a system wide economic saving to all consumers, and therefore does not represent a cross-subsidy between different consumers.
Impact on peak demand and network utilisation
Peak demand increases more slowly under the LGNC scenario. The largest reductions in peak demand growth are on the transmission and high voltage networks where peak demand is predicted to increase by 22-23% by 2050 under BAU but by only 8-11% under the LGNC scenario. This represents reductions in peak demand of over 50%.
Download comprehensive economic modelling results:
- Economic impact analysis of local generation network credits summary
- Economic impact analysis of local generation network credits in NSW: full report
What is the problem?
The current charging structure in the National Energy Market (NEM) in Australia reflects the historic reality of one-way flows of electricity from large centralised energy generators to consumers. This model has little flexibility to cater for today’s prosumer, who is interested in partial use of the distribution system, or to incentivise behaviour that can reduce electricity costs for everyone. Local network charges and Local Electricity were investigated in this project to further our understanding and help resolve these problems identified with the current market:
- Inefficient sizing and operation of distributed generators,
- Lack of incentive for dispatchable generators to operate at required (peak) times,
- Potential under-utilisation of the grid, with consequent rise in consumer charges, and
- Perverse incentives to duplicate infrastructure.
What is the solution?
This project brought together a partnership of consumers, researchers, electricity providers and government to research two mechanisms to support local energy – Local Network Charges for partial use of the electricity network, and Local Electricity Trading (LET) between associated customers and generators in the same local distribution area. The combination of these two mechanisms aims to offer desirable alternatives to customers who might otherwise choose to disconnect from the grid altogether or keep all their generation “behind the meter”, reducing the amount of electricity they take from the grid. This could reduce the overall network costs in a more distributed energy future.
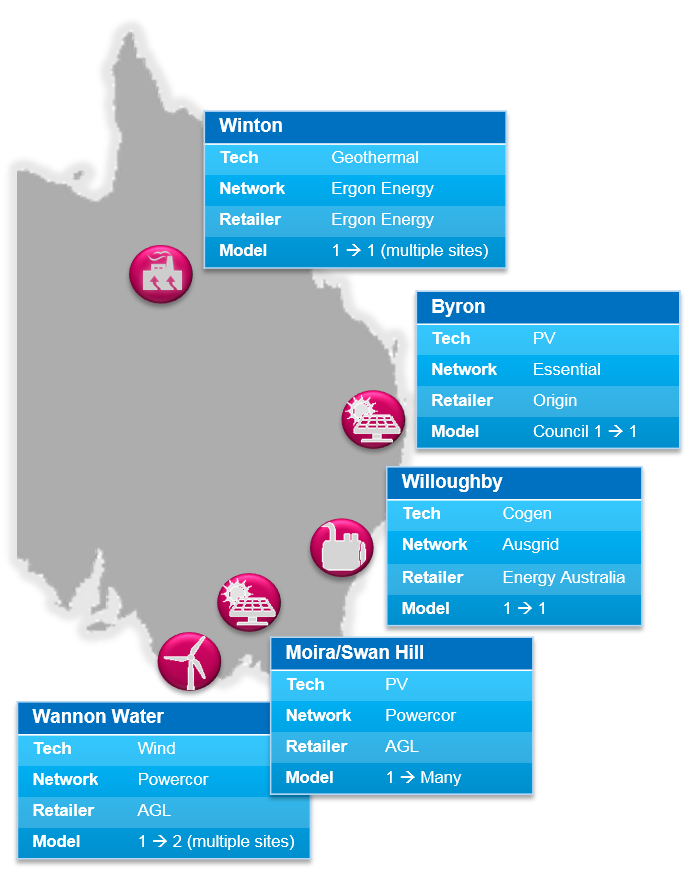
The project provides case study evidence from five ‘virtual trials’ of local network charges and local electricity trading, in NSW, VIC, and QLD; methodologies for calculating local network charges and economic modelling.
Trial Participants, locations and technologies
LGNC Rule change proposal
ISF worked with electricity sector stakeholders on making regulation fit for the future, and in particular through this project, on the Local Generation Network Credit (LGNC) rule change. On 23rd September 2016 the AEMC released draft determination to reject the LGNC Rule Change.
ISF hosted a webinar for organisations interested in making a submission on the AEMC’s draft determination on local generation network credits on Wednesday 26th October 2016. The presentations from the webinar are available for viewing:
Section 1 Background and trials results (19 minutes)
Section 2 What effect does an LGNC have on all consumers (8 minutes)
Section 3 Commentary on the draft rule change determination (17 minutes)
The draft ruling is a missed opportunity
The AEMC’s draft ruling unfortunately did not address the issues raised in the rule change proposal. It did nothing to change the current incentives to avoid using the grid as much as possible, and did not incentivise the benefits that distributed generators can offer. This was a missed opportunity for the Australian electricity sector to be on the front foot in developing an electricity grid fit for purpose in the 21st century. For further background a summary of the issue is presented in this media article.
Download the ISF submission on the rule change proposal:
What are Local Network Charges?
Local network charges are reduced network tariffs for electricity generation that is used within a defined local network area. In most circumstances, the tariff will reduce the network charge portion of electricity bills for local generators to the extent that the generation reduces long term network costs. This recognises that the generator is using only part of the electricity network, and reduces the network charge accordingly. To date reduced network tariffs have been applied most systematically in the UK.
What is Local Electricity Trading?
Following a period of research and consultation in 2015, we have decided to use the term ‘local electricity trading’ to describe the concept previously referred to as virtual net metering (VNM). Feedback demonstrated that although VNM has some recognition within the energy sector, it is not widely understood and the term does not convey the meaning of the concept.
Local Electricity Trading is an arrangement whereby generation at one site is “netted off” at another site on a time-of-use basis, so that Site 1 can ‘sell’ or assign generation to nearby Site 2. This will reduce the combined energy and retail portion of electricity bills for local generation.
RESEARCH OUTPUTS
Presentations
-
The Network Value of Distributed Generation - 13 October 2016
-
All Energy 2016 Conference - 4 October 2016
-
Local Energy and Microgrids Conference - 28 April 2016
-
Solar Energy Industries Association - 18 March 2016
-
AMEC LGNC Consultation workshop -15 March 2016
-
Australian Utility Week - 24 November 2015
-
All Energy 2015 Conference - 7 October 2015
-
Smart Future Cities Conference - 1 October 2015
-
Energy Storage World Forum - 15 September 2015
-
Clean Energy Summit presentation - 16 July 2015
Briefing papers and submissions
Trials results
- Local Network Charges and Local Electricity Trading: Byron Shire Council trial fact sheet
- Byron trial case study report
- Download the business case spreadsheet for the Byron virtual trial (large file 36MB) The business case spreadsheets from other trials are available on request.
- Local Network Charges and Local Electricity Trading: Wannon trial fact sheet
- Wannon trial case study report
- Local Network Charges and Local Electricity Trading: Willoughby trial fact sheet
- Willoughby trial case study report
- Local Network Charges and Local Electricity Trading: Winton trial fact sheet
- Winton trial case study report
Trials summary report
One to many LET trial report
- Virtual trial of local electricity trading and local network credits: a community solar farm
- Download the business case spreadsheet for the Moira and Swan Hill virtual trial. The business case spreadsheets from other trials are available on request.
Economic modelling results
- Economic impact analysis of local generation network credits summary
- Economic impact analysis of local generation network credits in NSW: full report
Local Network Credit methodology
- Methodology for Calculating a Local Network Credit (4.26MB)
- Towards a Method to Calculate a Local Network Credit
- Long Run Marginal Costs Methodology Paper (prepared by Energeia)
Other project papers and submissions
- Local Electricity Trading: Retailer Considerations
- Submission to AEMC on ERC0191: National Electricity Amendment (Local Generation Network Credits) Rule 2015
- Renewable power options enabled by local electricity trading
- Building a Level Playing field for Local Energy: Local Network Charges and Local Electricity Trading Explained
- Local Network Charges and Local Electricity Trading Market Scan
MEDIA
Media releases
-
New measures to unlock local energy potential could save electricity consumers $1bn, UTS media release 21 September 2016
-
Local electricity trading trial starts, Byron Council media release 2 December 2015
-
Building a level playing field for local energy consumers, UTS media release 15 June 2015
-
Investigating more flexible charges for local renewables, ARENA media release 15 June 2015
Articles
-
The A$1.2 billion saving Australia’s electricity rule-maker just knocked back, The Conversation, 28th September 2016.
-
City of Sydney request to change energy market rule all but rejected, Sydney Morning Herald, 25th September 2016.
-
Incumbents erect another barrier to solar, storage and shared energy. Renew Economy, 25th September 2016
-
AEMC says no on rewarding local energy sharing, and industry is dismayed, Fifth Estate, 22nd September 2016
-
Energy market rule-maker says no to real reform – again, Renew Economy, 22nd September 2016
-
Credit where it’s due: How distributed energy could save $1bn on grid costs, One step off the Grid, 20th September 2016
-
Levelling the playing field for local energy through tarrif reform, 27 April 2016
-
Incumbents tariff war on rooftop solar accelerates death spiral, RenewEconomy, 8 May 2016
-
Paris UN climate conference 2015: Clover Moore tells government to get out of the way SMH, 8 December 2015
-
Solar sharing trial underway in Byron NBN News, 2 December 2015
-
Energy sharing incentives could lead to more clean power and consumer savings Mozo, 4 November 2015
-
Proposed electricity network rule change to incentivise energy sharing, lead to consumer savings ABC News, 3 November 2015
-
Rooftop solar cap? Network suggests limit to regional PV installs RenewEconomy, 8 October 2015
-
City of Sydney, property groups push regulator to allow shared energy RenewEconomy, 17 July 2015
-
Virtual net metering to ease off-grid movement Energy Source & Distribution National, 1 July 2015
-
Thinking outside the square - virtual net metering could reduce power bills 25 June 2015
- Byron council in ‘power exchange’ trial Echo Net Daily, 19 June 2015
- Research project to build level playing field for local energy consumers The Fifth Estate, 16 June 2015
- Byron shire to be first in Australia to pilot virtual net metering RenewEconomy, 23 March 2015
Researchers
-
Research Director
-
Research Director
-
Research Director
-
Adjunct Fellow
-
Adjunct Associate Professor
-
 Jenni Downes
Jenni Downes
Years
- 2015-2016
Funded by
- Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA)
The project received additional funding from Ergon Energy, Moira Shire and Swan Hill Councils, Wannon Water, City of Sydney, Byron Shire Council, Willoughby Council and UTS and is supported in-kind by AGL, NSW Government Department of Industry, Powercor and Total Environment Centre